
The soma houses the cell nucleus and most of the genomic expression and synthetic machinery that elaborates the proteins, lipids, and sugars that constitute the neuronal cytoplasm and membranes. Neurons are generically characterized by a central cell body or soma that comes in different shapes. 3.6 Intrinsic electrical properties and subthreshold oscillations.Their ability to regulate extracellular background synaptic transmitter levels makes them, however, essential for CNS function. Their electrical response dynamics, being slow compared with that of neurons place them mostly in a modulatory role. It is now known that these cell types are essential in the maintenance of the neuronal network, in neuronal migration during development and in the generation of myelin.
Other cellular types are also present in the central nervous system (CNS), most particularly several types of glial elements, initially considered a glue type cell serving as a support matrix for the neuronal circuits. The anatomical variation of these neurons is large, but the general morphology and their electrical and ligand dependent responsiveness allows these cells to be classed as neurons (coined in 1891 by Wilhelm von Waldeyer).
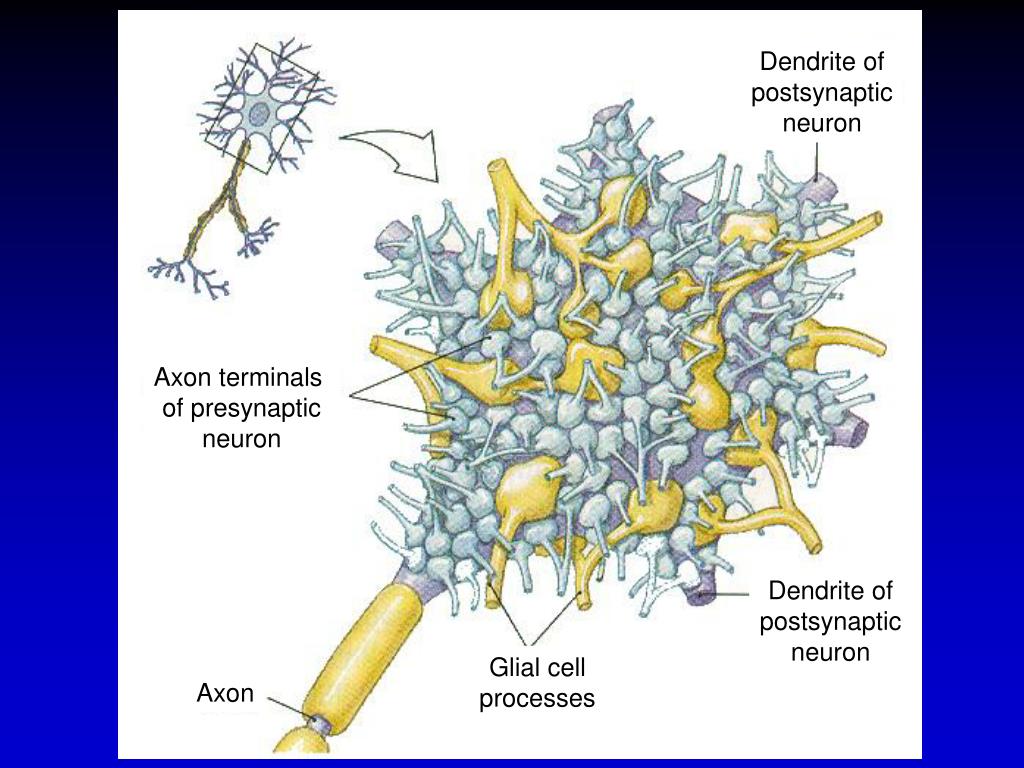
Neurons are the principal cellular elements that underlie the function of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, peripheral sensory systems and enteric (gut) nervous system. Cell sensitive to water movement in the medicinal leech, (Gascoigne & A McVean 1991). Figure 1: Drawings of neurons showing soma and dendrites in black, axon in red.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
